By Occupational Therapist Jimmy Roberts, OTD, OTR/L
What is CMC Arthritis?
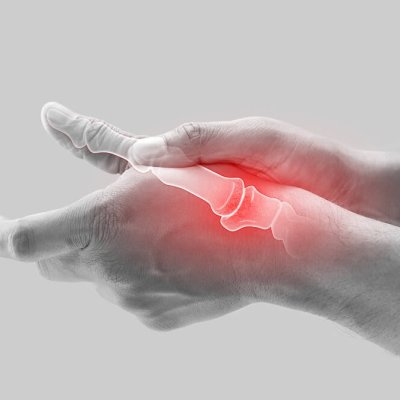
CMC arthritis, or carpometacarpal arthritis, affects the base of the thumb where it meets the wrist. It impacts the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, crucial for thumb movement and stability.
This condition occurs when the protective cartilage in the joint wears away, resulting in bone-on-bone contact and causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. CMC arthritis can affect anyone, but it is more common in women and typically develops with age.

Individuals with thumb CMC arthritis may experience symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, weakness, and aching pain. The pain worsens with activities involving gripping or repetitive thumb movements.
If you suspect you have CMC joint arthritis, consult with a hand therapist. They can provide an evaluation, diagnose CMC arthritis, and develop a personalized treatment plan to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Symptoms of CMC Arthritis
CMC arthritis can cause significant pain and discomfort. One common symptom is pain and discomfort in the thumb base, aggravated by activities requiring gripping or pinching motions. The pain may radiate to the wrist or forearm.
Swelling and tenderness are also typical symptoms of CMC arthritis. The joint may become inflamed and appear swollen, feeling tender to the touch.
Another noticeable symptom is the loss of grip strength and dexterity. As the condition progresses, the thumb joint becomes less stable, weakening the grip and making it difficult to hold objects firmly or perform fine motor tasks.
If you experience any of these symptoms, consulting with a hand therapist is essential. They can offer treatments to manage thumb CMC arthritis, including exercises, splinting, and other therapeutic interventions.
Treatments for CMC Arthritis
CMC arthritis can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased hand function. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to alleviate these symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Non-surgical options are often the first line of treatment for CMC joint arthritis. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, wearing a splint can provide relief and prevent further damage.
Physical and occupational therapy play a crucial role in managing CMC arthritis. Hand therapists can design a personalized exercise program to improve joint mobility, strength, and flexibility.
If non-surgical treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Arthroplasty involves removing damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial materials. Arthrodesis fuses the joint together, eliminating painful movement.
After surgery, a comprehensive recovery and rehabilitation process is essential. Your hand therapist will guide you through exercises and activities to regain strength, range of motion, and function.
Role of Hand Therapist in CMC Arthritis
A hand therapist plays a crucial role in managing thumb CMC arthritis, providing specialized care to help patients alleviate symptoms and improve hand function.
Hand therapists possess a deep understanding of the hand’s anatomy, enabling them to accurately diagnose and develop personalized treatment plans for CMC joint arthritis patients.
When it comes to pain management, hand therapists employ various therapeutic techniques to help alleviate discomfort. These may include manual therapy and modalities like heat and cold therapy.
In addition to pain management, hand therapists focus on hand exercises and rehabilitation strategies to improve hand function. They may use custom splints or braces to support and protect the affected joint during the rehabilitation process.
By working closely with patients, hand therapists create individualized treatment plans addressing their specific needs and goals.
If you seek effective treatment for CMC arthritis, consulting a hand therapist can help you regain hand function and improve your overall quality of life.